High Current, High Voltage BLDC controller with WIFI
- Rotem Segev
- Apr 10, 2023
- 2 min read
Updated: Jan 5, 2025
A unique 100V, 30A BLDC controller and driver with WIFI and Bluetooth!
Suitable for all types of Brushless DC motors.

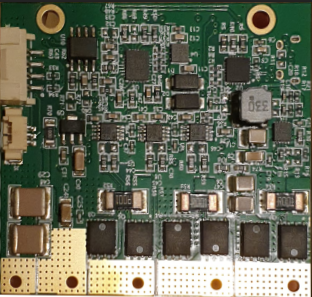
This board houses a complete BLDC driver + FOC controller + WIFI and Bluetooth that runs its own webserver for configurations and motor control.
General Features
· Industrial grade, high performance, brushless motor controller + driver
· 8-100V voltage input, 30A RMS (50A peak current)
· High performance 32bit dual core ARM 240MHz CPU
Control Methods
· Position, current and speed control loops
· Current loop update time: 62.5uS
· Brushless motor commutation: Hall sensor & encoder
· Field Oriented Control (FOC) algorithm
· 12-bit battery-less Absolute encoder
User Program
· 512KB fully customizable user program with hard - interrupt capability for the most demanding motion control needs & requirements.
· 8MB high speed memory
Communications interfaces
· 1 X UART port (Modbus RTU or any other customizable protocol – customer specific)
· 1 X USB programming port
· WIFI with TCP/IP support
· Bluetooth LE-V4.2
· PCB antenna for extended WIFI+BLE range
· Optional CANBUS communications
Monitoring functions
· Temperature sensor (RTD/PT100)
· Voltage (motor and logic)
· Current
· Errors (over current, under voltage, over voltage, position error, encoder error, over temperature)
ESP32 Webserver
Customizable UI for control, configurations, logging and graphing functions per customer's request
Functional Diagram

PID control functional diagram

Field Oriented Control
Field oriented control algorithm’s main task is to take user defined voltage uq and, by continuously reading the position of the motor rotor angle, calculate the appropriate phase voltages ua, ub and uc.

FOC algorithm calculates the phase voltages which create the magnetic field in the motor’s stator which are exactly 90 degrees “behind” the magnetic field of the permanent magnets of the rotor, creating a pushing effect. Here is a very nice animation of what happens inside of the motor when running simplified version of the the FOC called six-step modulation.
Sinusoidal modulation
Sinusoidal modulation is based on two transformation equations.

The waveform of the phases in sinusoidal commutation

Compared to the six-step commutation (trapezoidal drive), the sinusoidal current drive provides higher efficiency, lower torque ripple and lower acoustic noise. It is the preferred option by users for low-speed and lownoise motor control systems. For practical applications, both the maintenance and implementation cost are also a consideration in choosing the right motor type and motor controller.




Comments